Object-oriented programming is a programming paradigm that sees programs as a collection of objects interacting with each other. Objects are just containers for some data (called ‘fields’) and functions (called ‘methods’).
Object-oriented programming involves heavy usage of classes and enable us to make use of concepts like encapsulation, inheritance, polymorphism, etc.
Classes
TODO.
Static Classes
TODO.
Encapsulation
Encapsulation is about hiding the implementation details of a class as much as possible. Doing so will tend to minimise coupling.
Access modifiers Access modifiers are used to explicitly apply different levels of visibility to the members of a class. OO programming languages will usually give you the following 3 access modifiers.
private– only accessible within the class.protected– accessible within the class and within its subclasses.public– accessible by any class in the program.
Languages might have variations on how these access modifiers behave, as well as what the default visibility is when you omit the access modifier. Eg. In Java, a protected member is also visible to classes in the same package.
In general, prefer the most restricted visibility possible.
Inheritance
Inheritance (also called ‘subclassing’) is when you make one class derive from a base class, causing the child class to inherit the parent class’ non-private members.
Differences between languages Languages will have different syntax for inheritance and ways for subclasses to access their parent class. They may also differ in whether they support multiple inheritance or not.
- In C++, the inheritance might look like
class Sub : public Base. Note: C++ has concepts like private/public inheritance that other languges don’t have. - In JavaScript, inheritance looks like
class Sub extends Base. Within theSubclass, you have access the base class’ constructor and methods via thesuperkeyword. - In C#, inheritance looks like
public class Sub : Base. Subclasses can access the base class’ members through thebasekeyword (which is similar to JavaScript’ssuperkeyword).
Polymorphism
TODO.
Static Polymorphism
TODO.
Dynamic Polymorphism
TODO.
How does the program know which method is the correct one to invoke at runtime? tl;dr — in C++, every class with virtual functions has its own virtual function table (an array of function pointers) created at compile-time that holds pointers to that class’ virtual methods. Every object, on creation, gets a pointer to the function table of its class.
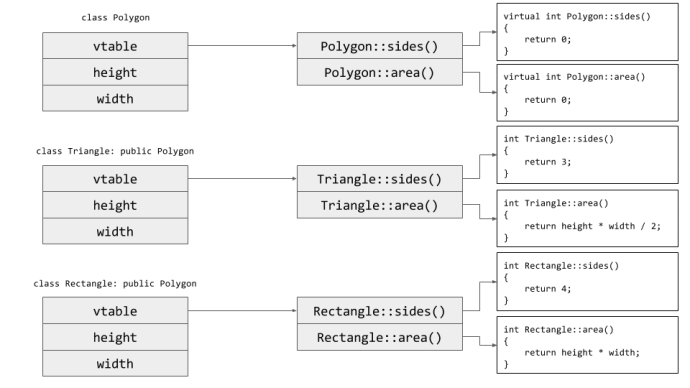 (sourced from Trail of Bits)
(sourced from Trail of Bits)
Method Overidding
Method overriding is when you make a subclass provide an implementation for a method that’s defined in its base class. Method overriding enables runtime polymorphism.
Differences between languages In many languages, overriding is implicitly done, but it’s recommended to explicitly label it.
- In TypeScript and C++, you can optionally add the
overridemodifier. - In Java, you can optionally annotate overridden methods with
@Override. - In C#, you must use the
overridemodifier.
Abstract Class
An abstract class is just one you can’t instantiate, forcing the user to choose and instantiate a specific concrete subclass that inherits from the abstract class.
Abstract classes let you define both concrete methods and abstract methods. If you find that you don’t need to define concrete methods, which is usually the majority of the time, then consider using an interface instead.
Differences between languages Making a class abstract differs between programming languages.
- In TypeScript, prefix a class with
abstract. - In C#, prefix a class with
abstract. - In C++, give the class at least one pure virtual function (i.e. an abstract method), eg.
virtual void foo() = 0;. There is noabstractkeyword.
Abstract Method
You can only define abstract methods inside an abstract class. Abstract methods are ones that must be overridden and implemented by the subclasses. If you want to provide a default implementation and allow for subclasses to optionally override a method, use virtual methods instead.
You cannot make abstract methods static.
Differences between languages To define abstract methods:
- In TypeScript, you’d use the
abstractmodifier. - In C#, you’d use the
abstractmodifier. - In C++, define a pure virtual function:
virtual void foo() = 0;.
Virtual Method
Virtual methods are methods that can be overridden by subclasses. To force subclasses to implement a method, use abstract methods instead.
- You cannot make virtual methods static.
Differences between languages To define virtual methods:
- In some languages like TypeScript and Java, methods are virtual by default. I.e. you can override methods by default — there’s no need to mark them as virtual.
- In C++, you’d use the
virtualmodifier, but it’s a little complicated because you can still override methods without it. See this StackOverflow post.
Interface
An interface is a ‘contract’ that defines what a user can do with the classes that implement that interface. You define the methods (and sometimes constants) that the interface supports, and then leave the implementation details to the subclasses. An interface is not a class, so you cannot instantiate it.
You cannot supply any implementation inside interfaces. If you want to provide some concrete methods, then consider using an abstract class instead. That being said, some programming languages like C# let you implement a static members inside an interface.
Differences between languages
- In TypeScript, you define an interface like this:
interface Blog { ... }, but it’s also used generally outside of OO design. - In C#, you define an interface like this:
public interface IFoo { ... }. - In C++, there is no native concept of interfaces, but you can simulate it by making an abstract class whose methods are all abstract, ie. all of them are pure virtual functions. Implementing an interface is therefore the same as inheritance. All interface members are public by default.